|
X-axis = Independent
- y-axis = Dependent
- Resistance - the oposition to move
- Friction - resistance to force
- Force - what is acting upon the object
- Air Friction
- Air friction, or air drag, is an example of fluid friction. Unlike the standard model of surface friction, such friction forces are velocity dependent. The velocity dependence may be very complicated,
and only special cases can be treated analytically. At very low speeds for small particles, air resistance is approximately
proportional to velocity and can be expressed in the form

where the negative sign implies that it is always directly opposite the velocity. For higher velocites and larger objects
the frictional drag is approximately proportional to the square of the velocity:

where 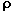 is the air density, A the crosssectional area, and C is a numerical drag coefficient. is the air density, A the crosssectional area, and C is a numerical drag coefficient.
-
Linear Velocity Dependence
- For objects moving at relatively low speeds through a liquid, where turbulence is
not a significant factor, then the viscous resistance to the object's motion is approximately proportional to its velocity. Even in gases
there are circumstances where the frictional resistance is approximately proportional to the velocity - such as the motion
of tiny dist particles through the air. More commonly, air friction has terms proportional to the square or even higher powers of the velocity.
- For linear velocity dependence the resistance force can be written
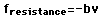 . If this resistance is the only force acting, then Newton's second law becomes . If this resistance is the only force acting, then Newton's second law becomes
- which will bring the object to rest in a distance
|
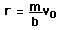 . . |
- If the weight W=mg of the object also acts, then the object approaches a terminal velocity :

This terminal velocity is expressed in terms of an effective value of g if the buoyant force is significant.
-
Fluid Friction
- The resistance to an object's motion through a fluid may be termed "fluid friction." It may take the form of viscous resistance in a liquid, or the rather different character of air friction when an object moves through a gas
Machines-
change the size and direction of a force.
 |
Machines make work easier or faster, but never produce more
work than is put into them. In fact, because of friction, more work is put into a machine than comes out! |
- There are 6 simple machines
 Inclined plane a slanted surface used to raise an object. Inclined plane a slanted surface used to raise an object.
 Wedge a moving inclined plane. Wedge a moving inclined plane.
|
- Force is multiplied since it is applied to a wide area and exerted
over a small area.
|
|
- The "sharper" the wedge, the greater the mechanical advantage.
|
 Screw an inclined plane wrapped around a cylinder. Screw an inclined plane wrapped around a cylinder.
 Lever a bar which can move freely around a fixed position, or fulcrum. Lever a bar which can move freely around a fixed position, or fulcrum.
- Experiment with a first-class lever.
- or chain wrapped around a wheel.
Continued on next page ...
|

